In the earlier chapters, we have seen the various Image files such as Centos which get downloaded from Docker hub from which you can spin up containers.
An example is again shown below.
If we use the Docker images command, we can see the existing images in our system. From the above screenshot, we can see that there are two images: centos and nsenter.
But Docker also gives you the capability to create your own Docker images, and it can be done with the help of Docker Files. A Docker File is a simple text file with instructions on how to build your images.
The following steps explain how you should go about creating a Docker File.
Step 1 − Create a file called Docker File and edit it using vim. Please note that the name of the file has to be "Dockerfile" with "D" as capital.
Step 2 − Build your Docker File using the following instructions.
FROM ubuntu
MAINTAINER demousr@gmail.com
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt-get install –y nginx
CMD [“echo”,”Image created”]
The following points need to be noted about the above file −
- The first line "#This is a sample Image" is a comment. You can add comments to the Docker File with the help of the # command
- The next line has to start with the FROM keyword. It tells docker, from which base image you want to base your image from. In our example, we are creating an image from the ubuntu image.
- The next command is the person who is going to maintain this image. Here you specify the MAINTAINER keyword and just mention the email ID.
- The RUN command is used to run instructions against the image. In our case, we first update our Ubuntu system and then install the nginx server on our ubuntu image.
- The last command is used to display a message to the user.
Step 3 − Save the file. In the next chapter, we will discuss how to build the image.
Docker - Building Files
We created our Docker File in the last chapter. It’s now time to build the Docker File. The Docker File can be built with the following command −
docker build
Let’s learn more about this command.
docker build
This method allows the users to build their own Docker images.
Syntax
docker build -t ImageName:TagName dir
Options
- -t − is to mention a tag to the image
- ImageName − This is the name you want to give to your image.
- TagName − This is the tag you want to give to your image.
- Dir − The directory where the Docker File is present.
Return Value
None
Example
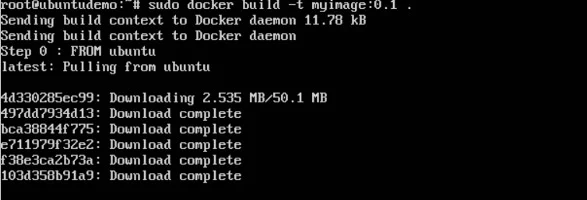
sudo docker build –t myimage:0.1.
Here, myimage is the name we are giving to the Image and 0.1 is the tag number we are giving to our image.
Since the Docker File is in the present working directory, we used "." at the end of the command to signify the present working directory.
Output
From the output, you will first see that the Ubuntu Image will be downloaded from Docker Hub, because there is no image available locally on the machine.
Finally, when the build is complete, all the necessary commands would have run on the image.
You will then see the successfully built message and the ID of the new Image. When you run the Docker images command, you would then be able to see your new image.
You can now build containers from your new Image.